Website speed optimization tips for SEO
In today’s fast-paced digital world, a slow website is more than just an annoyance—it’s a business killer. At Techgination, we understand that a lightning-fast website is crucial for SEO success. Not only does it improve user experience, but it also signals to search engines that your site is high-quality and worthy of ranking higher.
If you’re wondering why your website isn’t attracting the traffic and conversions you desire, slow loading times could be the culprit. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into website speed optimization tips that will boost your SEO and drive tangible results. Let’s get started!
Why Website Speed Matters for SEO
Before we delve into the tips, let’s understand why website speed is so vital for SEO:
- User Experience (UX): Users expect websites to load quickly. A slow site leads to frustration, higher bounce rates, and decreased engagement. Google prioritizes websites that provide a seamless user experience.
- Mobile-First Indexing: Google primarily indexes and ranks websites based on their mobile versions. Mobile users often have slower internet connections, making speed even more critical.
- Crawl Budget: Search engine crawlers have a limited “crawl budget.” Faster websites allow crawlers to index more pages within that budget, improving overall SEO.
- Ranking Factor: Google has explicitly stated that page speed is a ranking factor, especially for mobile searches. Faster websites tend to rank higher in search results.
- Conversion Rates: A faster website can significantly improve conversion rates. Users are more likely to complete a purchase or fill out a form if the process is quick and efficient.

1. Test Your Website Speed Regularly
Start by assessing your website’s current speed and identifying areas for improvement. Use the following tools:
- Google PageSpeed Insights: Provides a detailed report on mobile and desktop performance, including Core Web Vitals.
- GTmetrix: Offers comprehensive insights into loading speed, waterfall charts, and actionable recommendations.
- Pingdom Website Speed Test: Measures load times and identifies performance bottlenecks.
- WebPageTest: Allows you to test your website speed from different locations and devices.

2. Choose a High-Performance Hosting Provider
Your hosting provider has a massive impact on your website speed. A low-cost or shared hosting plan may save you money initially, but it can lead to slow loading times. Consider these hosting options:
- Shared Hosting: Suitable for small websites but has limited resources and slower speeds.
- VPS Hosting: A step up from shared hosting, offering better performance and resources.
- Dedicated Hosting: Provides exclusive resources for your website, ensuring faster load times.
- Cloud Hosting: Highly scalable and reliable, with excellent speed for websites of all sizes.

3. Enable Browser Caching
Browser caching stores static files (like CSS, JavaScript, and images) on a user’s device. When the user revisits your site, the browser loads these files locally instead of downloading them again.
- How to Enable Caching:
- For WordPress sites, use plugins like W3 Total Cache or WP Rocket.
- For Apache servers, add caching rules to the
.htaccessfile. - For Nginx servers, configure caching in the
nginx.conffile.
Example .htaccess code for caching:
<IfModule mod_expires.c>
ExpiresActive On
ExpiresByType image/jpg "access 1 year"
ExpiresByType image/jpeg "access 1 year"
ExpiresByType image/png "access 1 year"
ExpiresByType text/css "access 1 month"
ExpiresByType application/javascript "access 1 month"
</IfModule>
4. Optimize Images for Web Performance
Images are one of the largest contributors to slow-loading websites. To optimize them:
- Compress Images: Use tools like:
- TinyPNG or ImageOptim for manual compression.
- WordPress plugins like Smush or ShortPixel for automated image optimization.
- Use the Right Format:
- JPEG for photos and complex images.
- PNG for transparent backgrounds.
- WebP for a modern, lightweight format with excellent quality.
- Resize Images: Ensure images are appropriately sized for your website layout. Tools like Canva or Photoshop can help.

5. Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML
Minification reduces the size of your website’s code by removing unnecessary characters like spaces, comments, and line breaks. This makes the files smaller and faster to load.
- How to Minify:
- Use tools like UglifyJS (JavaScript), CSSNano (CSS), and HTMLMinifier (HTML).
- For WordPress, plugins like Autoptimize or WP Rocket simplify the process.
6. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN distributes your website’s static files (like images, CSS, and JavaScript) across servers worldwide. When a user accesses your site, the CDN serves the files from the server closest to their location, reducing latency.
- Popular CDN Providers:
- Cloudflare: Excellent free and premium plans.
- Akamai: Enterprise-grade performance.
- AWS CloudFront: Highly scalable and reliable.
Pro Tip: We recommend using a CDN for websites with global audiences to improve load times for users in different geographic regions.

7. Reduce HTTP Requests
Each element on your webpage (e.g., scripts, stylesheets, and images) requires an HTTP request to load. The more requests, the slower your website. Reduce HTTP requests by:
- Combining Files: Merge multiple CSS and JavaScript files into a single file.
- Eliminating Unnecessary Plugins: Deactivate and delete plugins you no longer use.
- Using CSS Sprites: Combine multiple small images into a single file and use CSS to display specific sections.

8. Enable GZIP Compression
GZIP compression significantly reduces the size of your website files, making them faster to transfer. Here’s how to enable it:
- For Apache Servers:
Add the following code to your.htaccessfile:
apache
IfModule mod_deflate.c> AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/html text/plain text/xml text/css text/javascript application/javascript application/json </IfModule>
- For Nginx Servers:
Add this to yournginx.conffile:
nginx
gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript;

9. Optimize Your Database
Cluttered databases can slow down your website. Regularly clean and optimize your database by:
- Deleting old revisions, spam comments, and unused data.
- Using database optimization plugins like WP-Optimize or Advanced Database Cleaner.

10. Enable Lazy Loading for Images and Videos
Lazy loading delays the loading of images and videos until they are visible in the user’s viewport. This reduces the initial page load time, especially for media-heavy websites.
- WordPress Solution: Use plugins like Lazy Load by WP Rocket or A3 Lazy Load.
- Manual Implementation: Add the
loading="lazy"attribute to your image or iframe tags.
Example:
<img src="example.jpg" loading="lazy" alt="Optimized Image">
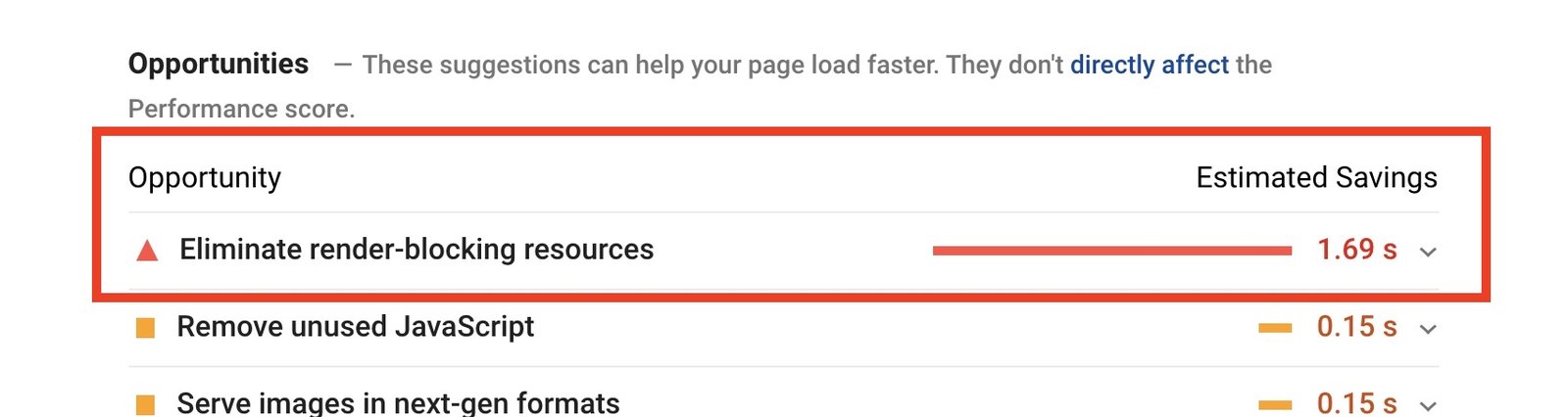
11. Eliminate Render-Blocking Resources
Render-blocking resources like CSS and JavaScript files can delay the loading of your webpage. To fix this:
- Defer JavaScript: Use the
deferorasyncattribute for non-critical JavaScript files. - Load Critical CSS Inline: Inline the CSS required for above-the-fold content and defer other stylesheets.
Example:
<script src="example.js" defer></script>
12. Upgrade to HTTP/2 or HTTP/3
HTTP/2 and HTTP/3 are faster versions of the HTTP protocol, offering better compression, multiplexing, and reduced latency. Most modern servers support these protocols. Check with your hosting provider to enable them.

13. Optimize Mobile Performance
With Google’s mobile-first indexing, optimizing your website for mobile devices is non-negotiable. Steps to improve mobile speed include:
- Responsive Design: Use CSS and frameworks like Bootstrap to ensure your site adapts to all screen sizes.
- Optimize Mobile Images: Use smaller image sizes for mobile devices.
- Test with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test: Ensure your site is fully optimized for mobile users.

14. Monitor and Optimize Third-Party Scripts
Third-party scripts (e.g., ads, analytics, or social media widgets) can slow down your site. To reduce their impact:
- Only include necessary scripts.
- Load scripts asynchronously.
- Use tag management systems like Google Tag Manager to control script loading.

15. Regularly Monitor and Maintain Website Performance
Website optimization is an ongoing process. Regularly monitor performance using tools like Google Analytics, Search Console, and heatmap tools like Hotjar. Address any issues as they arise to ensure consistent speed.
Conclusion
Optimizing your website speed is a powerful way to improve your SEO rankings, enhance user experience, and boost conversions. By following these detailed tips, you can ensure your website performs at its best. At Techgination, we specialize in creating fast, responsive, and SEO-friendly websites. Whether you need help with development, image optimization, or digital marketing, we’re here to help.
Contact Techgination today to supercharge your website’s performance and dominate the search results!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Website speed is a crucial ranking factor for search engines like Google. Faster websites improve user experience, reduce bounce rates, and increase conversions, helping with better search rankings.
Google recommends that a website should load in under 3 seconds for the best user experience and SEO performance.
You can test your website speed using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, Pingdom, and Lighthouse (Chrome DevTools).
Use image compression tools like TinyPNG or ShortPixel, and convert images to next-gen formats (WebP, AVIF) for better performance.
Browser caching stores website files on a visitor’s device, allowing faster loading times for repeat visits.
You can enable Gzip compression via your .htaccess file (Apache) or server settings (Nginx). WordPress users can enable it using caching plugins like WP Rocket or W3 Total Cache.
Yes, using too many plugins—especially poorly coded ones—can increase HTTP requests and database load, slowing down your site.
Lazy loading delays the loading of images and videos until they are needed, reducing initial page load time and improving performance.
It’s best to regularly monitor your website speed using tools like GTmetrix and Google PageSpeed Insights and apply necessary optimizations at least once every few months.

